The terms "race" and "ethnicity" are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings and connotations. While both concepts relate to human identity and categorization, they differ significantly in their origins, implications, and social contexts. In this article, we will delve into the differences between race and ethnicity, exploring why these distinctions are essential and why they can be challenging to grasp.
Defining Race and Ethnicity
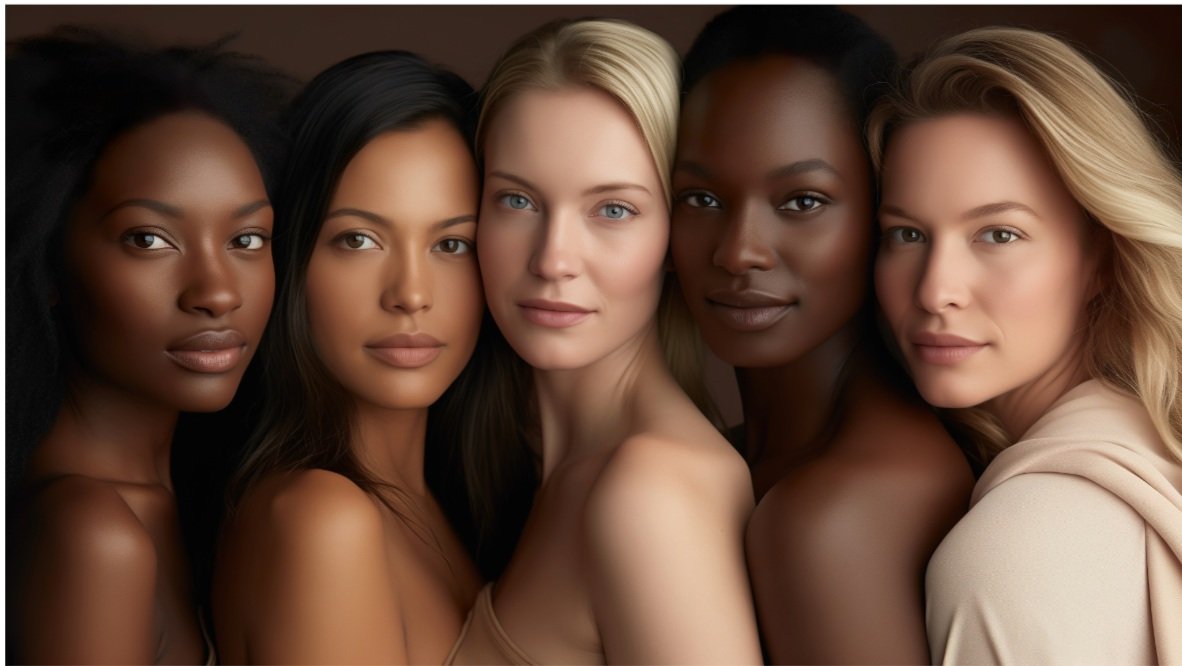
Race refers to the biological and physical characteristics that distinguish one group of people from another, such as skin color, hair texture, and facial features. Historically, the concept of race was used to categorize people into distinct groups, often with the intention of justifying social hierarchies and inequalities. However, modern science has discredited the idea of biological races, recognizing that human genetic variation is complex and cannot be reduced to simplistic categories.
On the other hand, ethnicity encompasses a broader range of factors, including cultural heritage, language, traditions, and national origin. Ethnicity is often tied to a shared sense of identity, history, and community, and can be a source of pride and belonging for individuals and groups.
Key Differences between Race and Ethnicity
While both race and ethnicity are social constructs, there are significant differences between the two:
Biological vs. Cultural: Race is often associated with biological characteristics, whereas ethnicity is rooted in cultural and social factors.
Fixed vs. Fluid: Race is often perceived as a fixed category, whereas ethnicity can be more fluid and context-dependent.
External vs. Internal: Race is often imposed upon individuals by external factors, such as societal norms and institutions, whereas ethnicity is often a self-identified aspect of one's identity.
Why the Distinctions Matter
Understanding the differences between race and ethnicity is crucial for several reasons:
Avoiding Reductionism: By recognizing the complexities of human identity, we can avoid reducing individuals to simplistic categories or stereotypes.
Promoting Inclusivity: Acknowledging the diversity of ethnic experiences and cultural backgrounds can help foster a more inclusive and equitable society.
Addressing Systemic Inequalities: Recognizing the intersections of race and ethnicity can help us better understand and address the systemic inequalities and biases that affect marginalized communities.
Challenges in Understanding the Distinctions
Despite the importance of understanding the differences between race and ethnicity, there are several challenges that make it difficult:
Linguistic and Cultural Barriers: The terms "race" and "ethnicity" are often used inconsistently or incorrectly, leading to confusion and misunderstandings.
Social and Historical Contexts: The meanings and implications of race and ethnicity vary across different social and historical contexts, making it challenging to develop a nuanced understanding.
Personal and Collective Biases: Our individual and collective biases can influence our perceptions of race and ethnicity, leading to oversimplifications or misconceptions.
In conclusion, the distinctions between race and ethnicity are essential for promoting a more nuanced understanding of human identity and experience. By recognizing the complexities and differences between these concepts, we can work towards a more inclusive and equitable society, one that values and celebrates the diversity of human cultures and backgrounds. Ultimately, unpacking the complexities of race and ethnicity requires a willingness to listen, learn, and engage in ongoing dialogue and self-reflection.